China's first commercial spacecraft launch site in Hainan to commence normalized launch missions in 2024
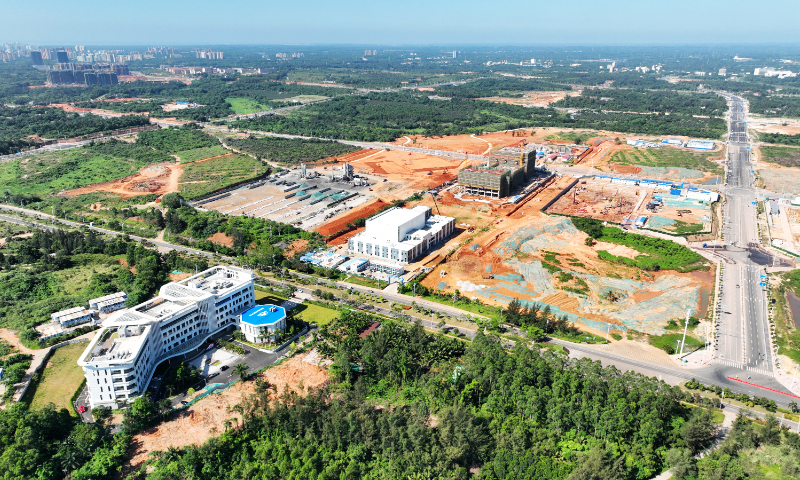

China's first commercial spacecraft launch site in Wenchang, South China's Hainan Province, is ramping up the final stages of construction, and plans to commence normalized commercial launch operations in 2024, a representative from the launch site told the Global Times on Wednesday.
The construction of the commercial spacecraft launch site began in July 2022, and the infrastructure needed for the site will be finished by the end of 2023. The first commercial launch mission will commence in the first half of 2024, and the launch site will enter the operations and normalized launch mission in the same year.
"According to current plan, the commercial launch site will commence launch missions at a high frequency in 2025, which means commercial launch missions will occur each month," Dong Chenghua, a representative from the administration bureau of the Wenchang International Aerospace City, where the commercial launch site locates, told the Global Times on Wednesday.
On April 13, 2018, China announced a decision to support Hainan in developing the whole island into a pilot free trade zone and gradually exploring and steadily promoting the establishment of a free trade port (FTP) with Chinese characteristics. By the end of 2025, the Hainan FTP is scheduled to initiate independent customs operations throughout the whole island according to a master plan released by the central authorities in 2020.
As one of the 13 key projects of the island, the Wenchang International Aerospace City will support the Hainan FTP construction from sectors of aerospace and relevant industries.
During 2015 to 2021, the scale of China's commercial spacecraft launch industry realized an average annual growth rate of 22.3 percent, and may hit 2.3 trillion yuan ($320 billion) in market size by 2024, industry data revealed.
Another representative from the administration bureau told the Global Times that the commercial spacecraft launch is in great demand among domestic private enterprises at present, which is mostly used in communication, remote control and navigation.
The Wenchang aerospace launch site is China's only coastal launch site with multiple natural advantages such as lower geographic latitude, less transport restrictions and high security for landing sites, which will largely reduce the cost for commercial spacecraft launch.
The launch site has facilitated multiple key launch missions including the China's space station Tiangong and the lunar probe Chang'e.
In addition, Wenchang commercial spacecraft launch site may have chance to explore the commercial launch market among Southeast Asian countries based on Hainan's geographic advantages.